Nasal Adenocarcinoma in Dogs: The Complete Owner’s Guide to Early Detection and Treatment Success
When your beloved canine companion starts showing persistent nasal discharge or breathing difficulties, it’s natural to worry. While many respiratory symptoms in dogs stem from minor infections or allergies, some cases point to a more serious condition: nasal adenocarcinoma. This aggressive form of nose cancer in dogs affects thousands of pets annually, but early detection and proper treatment can significantly improve your dog’s quality of life and survival outcomes.
This comprehensive guide reveals everything you need to know about canine nasal adenocarcinoma, from recognizing the earliest warning signs to understanding cutting-edge treatment options that are giving dogs longer, more comfortable lives.
Understanding Nasal Adenocarcinoma: The Most Common Nose Cancer in Dogs
Nasal adenocarcinoma represents the most frequently diagnosed type of nasal tumor in canines, accounting for approximately 60-70% of all nose cancers in dogs. Nasal tumors comprise approximately 2% of all cancers seen in dogs, making this a relatively uncommon but serious condition that requires immediate veterinary attention.
This malignant tumor originates from the glandular tissue lining your dog’s nasal passages and sinuses. Unlike many other cancers that spread rapidly throughout the body, nasal adenocarcinoma tends to be locally aggressive, meaning it destroys surrounding tissue but rarely metastasizes to distant organs initially.
Key Characteristics of Canine Nasal Adenocarcinoma
The unique behavior of this cancer type makes it both challenging and somewhat manageable:
Local Aggression: The tumor grows aggressively within the nasal cavity, potentially destroying bone, cartilage, and soft tissues in the surrounding area.
Limited Metastasis: In most cases, the cancer remains localized to the nasal region for extended periods, though it may eventually spread to nearby lymph nodes, lungs, or brain tissue.
Age Factor: Most diagnoses occur in senior dogs, with the average age at diagnosis being 10 years old.
Breed Predisposition: Certain breeds show higher susceptibility, particularly those with longer nasal passages.
Early Warning Signs: Recognizing Nasal Adenocarcinoma Symptoms in Dogs
The challenge with nasal adenocarcinoma lies in its subtle early symptoms, which often mimic common respiratory conditions. Understanding the progression of signs can help you seek veterinary care before the tumor advances to later stages.

While persistent sneezing may initially lead owners to try antihistamines, it’s important to consult a vet—learn about safe options like Benadryl (diphenhydramine), its appropriate uses, risks, and alternatives in this detailed guide.
Primary Symptoms to Monitor
Persistent Nasal Discharge The most common initial symptom is chronic nasal discharge that doesn’t respond to standard treatments. This discharge may appear as:
- Clear, watery secretions in early stages
- Bloody or rust-colored discharge as the tumor grows
- Thick, mucus-like consistency
- Typically affecting one nostril initially, later becoming bilateral
Progressive Breathing Changes As the tumor expands within the nasal cavity, you may notice:
- Increased snoring or noisy breathing
- Difficulty breathing through the nose
- Open-mouth breathing, even at rest
- Sneezing fits that seem excessive or unusual
Facial Changes and Deformities Advanced tumors can cause visible changes to your dog’s face:
- Swelling around the muzzle or nose area
- Asymmetrical facial appearance
- Bulging or protruding eyes
- Changes in the shape of the nasal bridge
Secondary Symptoms Indicating Progression
Neurological Signs If the tumor spreads to the brain, you might observe:
- Sudden onset of seizures
- Behavioral changes or disorientation
- Loss of coordination
- Sudden blindness
Systemic Effects
- Loss of appetite due to decreased sense of smell
- Weight loss
- General lethargy or decreased activity
- Difficulty eating or drinking
Risk Factors: What Increases Your Dog’s Chances of Developing Nasal Cancer
Understanding risk factors helps dog owners make informed decisions about prevention strategies and early screening, especially for high-risk breeds.
Environmental Risk Factors
Airborne Pollutants and Carcinogens Research has identified several environmental factors that increase nasal cancer risk:
- Tobacco smoke exposure: Dogs living with smokers face elevated risk
- Urban air pollution: Higher incidence rates in dogs living in polluted cities
- Industrial chemicals: Exposure to kerosene, coal combustion products
- Household chemicals: Including certain flea sprays and aerosols
Geographic and Living Conditions
- Urban environments show higher incidence rates than rural areas
- Indoor dogs exposed to cleaning chemicals and air fresheners
- Dogs living near industrial areas or heavy traffic
Genetic and Breed Predispositions
Certain breeds demonstrate significantly higher susceptibility to nasal adenocarcinoma:
High-Risk Breeds:
- Airedale Terriers: Among the highest risk breeds
- Scottish Terriers: Significant genetic predisposition
- Basset Hounds: Long nasal passages increase vulnerability
- Collies and Sheepdogs: Moderate to high risk
- German Shorthaired Pointers: Higher incidence in sporting breeds
- Golden and Labrador Retrievers: Popular breeds with notable risk
Anatomical Factors:
- Longer-nosed breeds (dolichocephalic) face higher risk
- Nasal passage length provides more surface area for tumor development
- Male dogs show slightly higher incidence rates than females
Comprehensive Diagnosis: Modern Approaches to Detecting Nasal Cancer
Accurate diagnosis of nasal adenocarcinoma requires sophisticated imaging and sampling techniques that have evolved significantly in recent veterinary medicine.
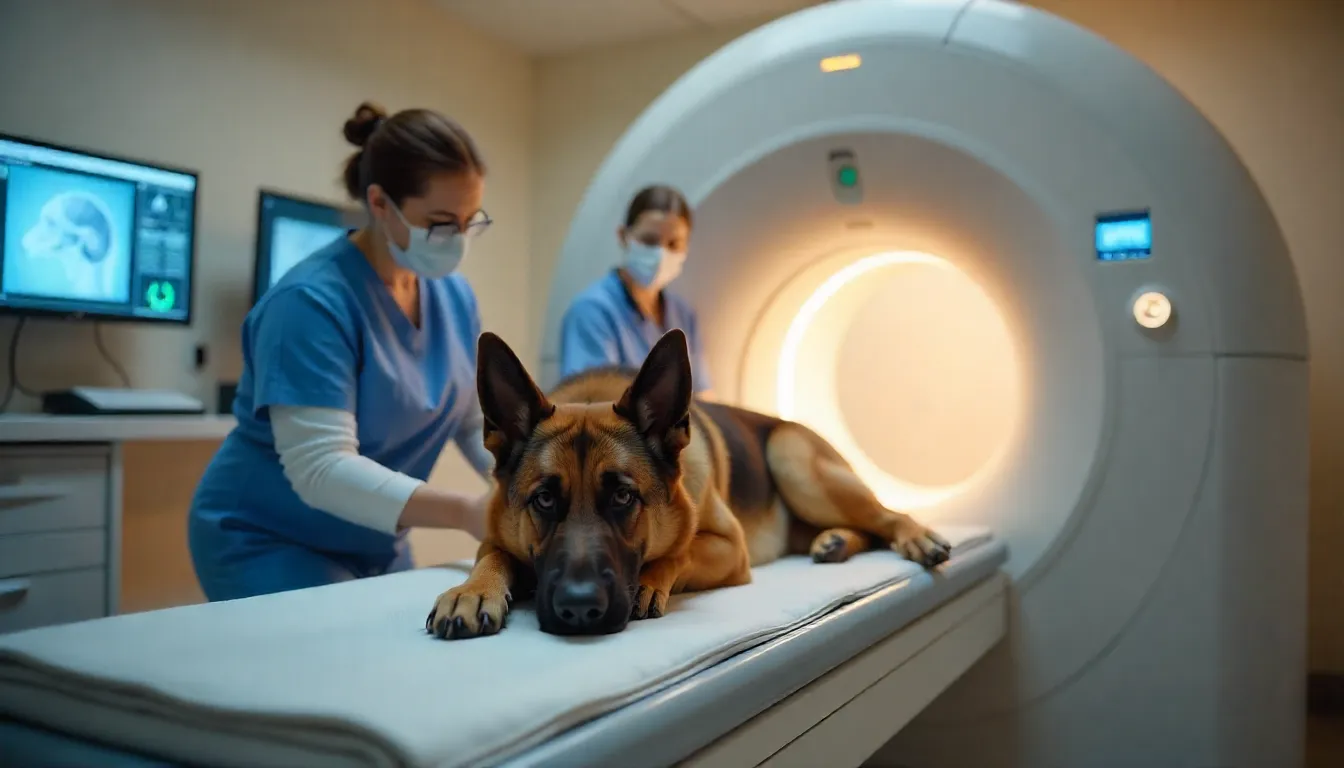
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Computed Tomography (CT) Scanning CT scanning has become the gold standard for nasal tumor diagnosis because it provides:
- Detailed visualization of tumor extent and location
- Assessment of bone destruction or invasion
- Evaluation of potential spread to surrounding structures
- Precise treatment planning for radiation therapy
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Some veterinary facilities now offer MRI for nasal tumor evaluation:
- Superior soft tissue contrast compared to CT
- Better visualization of brain involvement
- Detailed assessment of treatment response
Histopathological Confirmation
Tissue Biopsy Procedures Definitive diagnosis requires obtaining tissue samples through:
- Rhinoscopy: Direct visualization and sampling through the nasal passages
- Surgical biopsy: More invasive but provides larger tissue samples
- Fine needle aspiration: Less invasive initial sampling method
Staging and Metastasis Evaluation Complete staging includes:
- Chest radiographs to check for lung metastasis
- Regional lymph node evaluation
- Blood work to assess overall health status
Revolutionary Treatment Options: Hope for Dogs with Nasal Adenocarcinoma
For nasal tumors, radiation therapy is the preferred standard of treatment for dogs, but modern veterinary oncology offers several approaches that can significantly extend and improve your dog’s life.

Radiation Therapy: The Gold Standard Treatment
Conventional Radiation Therapy Traditional radiation treatment involves:
- Multiple treatment sessions (typically 15-20 treatments)
- Daily treatments over 3-4 weeks
- Requires general anesthesia for each session
- Excellent tumor control rates
Stereotactic Radiation Surgery (SRS) The latest advancement in radiation therapy offers:
- Fewer treatments: Often completed in 1-3 sessions
- Higher precision: Minimal damage to healthy tissue
- Improved outcomes: Better tumor control with fewer side effects
- Reduced anesthesia risk: Fewer anesthetic episodes
Surgical Interventions
Debulking Surgery While complete surgical removal is rarely possible, debulking procedures can:
- Remove accessible tumor tissue
- Improve nasal airflow
- Reduce symptoms
- Enhance radiation therapy effectiveness
Combination Approaches Many veterinary oncologists now recommend:
- Surgery followed by radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy as an adjunct treatment
- Palliative procedures to maintain quality of life
Emerging Treatment Modalities
Immunotherapy Research into immune-based treatments shows promise:
- Stimulating the dog’s immune system to fight cancer
- Potential for longer remission periods
- Reduced side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy
Targeted Therapy Development of drugs that specifically target cancer cells:
- Precision medicine approaches
- Personalized treatment based on tumor characteristics
- Improved outcomes with fewer side effects
Prognosis and Life Expectancy: What to Expect
Understanding prognosis helps families make informed decisions about treatment and quality of life considerations.
Survival Statistics and Outcomes
With Treatment:
- Median survival time: 18-24 months with radiation therapy
- Some dogs achieve 3-5 years, considered essentially cured
- Quality of life typically remains good during treatment and remission
Without Treatment:
- Median survival time: 3-5 months after diagnosis
- Progressive symptoms severely impact quality of life
- Palliative care becomes the primary focus
Factors Affecting Prognosis
Positive Prognostic Factors:
- Early stage at diagnosis
- Good overall health status
- Absence of metastasis
- Response to initial treatment
Challenging Prognostic Factors:
- Advanced local disease with bone destruction
- Evidence of metastasis
- Poor response to radiation therapy
- Concurrent health issues
Managing Your Dog’s Care: Recovery and Long-term Support
Successful management of nasal adenocarcinoma extends beyond medical treatment to encompass comprehensive supportive care.

During treatment, creating a calm, prepared environment can be lifesaving—refer to this pet survival guide for essential tips on safely managing emergencies.
Post-Treatment Care
Monitoring for Side Effects Radiation therapy may cause:
- Temporary skin irritation around the treated area
- Possible hair color changes (permanent)
- Mild fatigue during treatment period
- Oral discomfort requiring special diet considerations
Follow-up Protocols Regular monitoring includes:
- Periodic imaging to assess treatment response
- Physical examinations every 3-6 months
- Blood work to monitor overall health
- Quality of life assessments
Quality of Life Considerations
Environmental Modifications
- Air purification systems to reduce irritants
- Humidification to ease nasal discomfort
- Quiet, stress-free recovery spaces
- Easy access to food and water
Nutritional Support
- High-quality, easily digestible diets
- Appetite stimulants if needed
- Nutritional supplements to support immune function
- Adequate hydration maintenance
Prevention Strategies: Protecting Your Dog’s Health
While nasal adenocarcinoma cannot be completely prevented, several strategies can reduce your dog’s risk.
Environmental Risk Reduction
Indoor Air Quality Management
- Eliminate tobacco smoke exposure
- Use air purifiers with HEPA filters
- Choose natural cleaning products when possible
- Ensure proper ventilation in living spaces
Outdoor Exposure Considerations
- Limit time in heavily polluted areas
- Avoid walking during high pollution periods
- Consider protective measures in urban environments
- Regular grooming to remove environmental contaminants
Early Detection Programs
Regular Veterinary Checkups
- Annual examinations for all dogs
- Semi-annual checkups for senior dogs
- Immediate evaluation of persistent nasal symptoms
- Breed-specific screening for high-risk dogs
Frequently Asked Questions About Canine Nasal Adenocarcinoma
Hope and Quality of Life for Dogs with Nasal Adenocarcinoma
A diagnosis of nasal adenocarcinoma in your dog isn’t the end of the road—it’s the beginning of a treatment journey that can provide months to years of quality time together. With advances in veterinary oncology, particularly in radiation therapy techniques and supportive care, many dogs with this condition continue to enjoy active, comfortable lives.
The key to the best possible outcome lies in early detection, prompt veterinary care, and working closely with a veterinary oncologist to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your dog’s specific needs. While nasal adenocarcinoma presents challenges, understanding the condition empowers you to make informed decisions that prioritize your dog’s comfort and well-being.
Remember that every dog responds differently to treatment, and hope exists even in challenging cases. With proper medical care, environmental modifications, and dedicated supportive care, your dog can continue to be a cherished member of your family while battling this condition.
If you suspect your dog may be showing signs of nasal adenocarcinoma, don’t wait—early intervention offers the best chance for successful treatment and extended quality of life. Contact your veterinarian immediately to discuss evaluation options and begin the path toward the most effective treatment plan for your beloved companion.







