Heartworm Disease in Dogs: Prevention, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Heartworm disease is a serious health threat to dogs caused by a parasite known as Dirofilaria immitis. This foot-long worm lives in the heart and lungs of infected dogs, leading to severe health issues. Recognizing the signs and understanding how heartworm disease spreads is crucial for every dog owner.

Mosquitoes play a key role in the transmission of this disease, making it essential to protect dogs from bites. Annual testing and preventive medication can help guard against this potentially fatal condition. Awareness about the symptoms and stages of infection will equip pet owners to act quickly and ensure their dog’s safety.
With the right knowledge and preventive measures, dog owners can keep their pets healthy and free from heartworm disease. Understanding the risks and treatment options is vital in taking proactive steps against this hidden danger.
Heartworm Life Cycle and Transmission
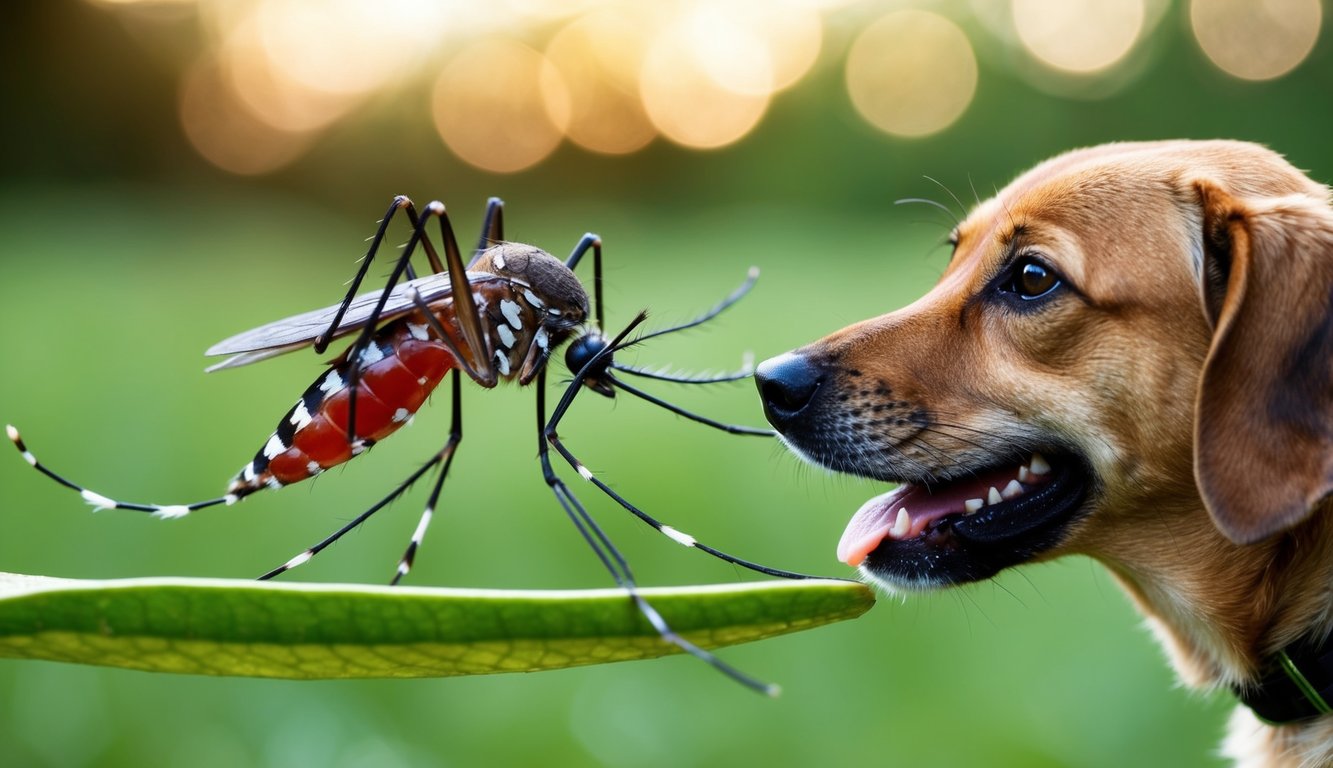

Heartworm disease in dogs involves a complex life cycle primarily facilitated by mosquitoes. Understanding how heartworms grow and spread can help in prevention and treatment efforts. The following subsections explain the essential role mosquitoes play and the various stages of the heartworm life cycle.
The Role of Mosquitoes in Heartworm Disease
Mosquitoes are key players in the transmission of heartworms. An infected mosquito bites a dog and takes in microfilaria, which are tiny heartworm larvae present in the dog’s bloodstream. Inside the mosquito, the microfilaria develop into infective larvae over about 10 to 14 days.
When this mosquito bites another dog, it transfers the infective heartworm larvae through its saliva. This process initiates the heartworm infection cycle in the new host. Without mosquitoes, heartworms cannot spread effectively, making them vital to the disease’s life cycle.
Lifecycle Stages of Heartworm
The life cycle of heartworms consists of several stages. First, the microfilariae circulate in the bloodstream of the infected dog. These microfilariae grow into heartworm larvae inside a mosquito after it feeds on the dog’s blood.
The larvae, now known as infective larvae, are transmitted when the mosquito bites another dog. Once inside, these larvae migrate to the heart and lungs, maturing into adult heartworms. This entire process can take around six months.
Adult heartworms can live for five to seven years in a dog, reproducing and releasing new microfilariae back into the bloodstream. This perpetuates the cycle of infection, highlighting the importance of prevention methods such as regular veterinary check-ups and heartworm medications.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Heartworm disease can show various symptoms in dogs, but early signs may be hard to notice. As the disease progresses, symptoms become more pronounced, and proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
Recognizing Heartworm Symptoms
Dogs with heartworm disease may display several signs. Common symptoms include:
- Weight Loss: Affected dogs often lose weight despite normal appetite.
- Exercise Intolerance: They may struggle with physical activities they previously enjoyed.
- Lethargy: Increased tiredness or lack of energy can be apparent.
- Labored Breathing: Dogs may breathe heavily or show signs of distress.
- Swollen Belly: In advanced cases, excess fluid can cause noticeable swelling.
These symptoms usually develop gradually. Early detection is important, as many dogs do not show any signs in the early stages.
Diagnostic Tests for Heartworm Infection
Diagnosing heartworm disease involves several tests. Blood tests are the most common method. An antigen test detects proteins released by adult female heartworms.
Other important diagnostic tools include:
- Chest X-rays: These help to identify any heart or lung issues caused by the infection.
- Echocardiography: This ultrasound test provides a clear image of the heart, allowing veterinarians to visualize heartworms directly.
Through these tests, veterinarians can determine the extent of the infection and how best to treat it. Early diagnosis leads to better outcomes for affected dogs.
Prevention and Treatment Strategies

Preventing heartworm disease in dogs is crucial to their health. Early diagnosis and treatment can save lives. The following sections cover how veterinarians diagnose the disease, the importance of prevention, available preventive medications, and treatment options.
How Veterinarians Diagnose Heartworm Disease in Dogs
Veterinarians diagnose heartworm disease primarily through blood tests. The most common test detects specific proteins released by adult female heartworms. This test is usually done annually for dogs, even if they are on preventive medications.
Additional testing may include a complete blood count and X-rays of the chest. X-rays can show changes in the heart and lungs caused by heartworms. If heartworm infection is suspected, a veterinarian may suggest further tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Importance of Prevention
Prevention is the best strategy against heartworm disease. It is much simpler and less costly than treatment. Heartworm disease is transmitted by mosquito bites, so minimizing exposure to mosquitoes is also important.
Using preventive medications is key. These medications come in various forms, including pills, topical treatments, and injectables. They effectively kill any heartworm larvae before they mature into adults. Regular use of these medications protects dogs from the disease.
Available Heartworm Preventives
Heartworm preventives vary in type and formulation. Some common heartworm medications include:
- Ivermectin: A monthly tablet that is widely used.
- Milbemycin: Another oral option, also given monthly.
- Selamectin: A topical treatment applied monthly.
- Moxidectin: Available as a monthly topical or a six-month injectable.
It is critical for pet owners to follow veterinarian recommendations on dosage and administration. Regular testing confirms that the prevention strategy is effective.
Heartworm Treatment Options
If a dog tests positive for heartworms, prompt treatment is necessary. The primary treatment for adults involves the administration of melarsomine. This medication kills adult heartworms and requires careful monitoring.
In addition to melarsomine, doxycycline may be used to treat the infection. This helps eliminate accompanying bacteria that can worsen health problems. The treatment protocol often spans several months, requiring follow-up visits for monitoring.
Veterinarians will provide advice on recovery and activity limits during treatment. This approach helps prevent complications and ensures the dog returns to good health.
Additional Considerations and Veterinary Care

Care for a heartworm-positive dog involves careful management and attention to veterinary care. Understanding the potential complications and the necessary post-treatment steps is vital for the dog’s health and recovery.
Managing Heartworm Positive Dogs
Managing a heartworm-positive dog requires regular veterinary visits and monitoring. The veterinarian may suggest a treatment plan based on the severity of the infection.
Key Points:
- Additional diagnostics like blood tests and X-rays may be necessary.
- Monitoring for risk factors, such as age and existing health problems, is crucial.
Treatment involves:
- Administration of heartworm medication to kill adult worms.
- Restricting exercise to reduce stress on the heart and lungs.
Close observation of symptoms related to pulmonary hypertension is essential. This condition can arise due to increased pressure in the blood vessels of the lungs.
Post-Treatment Care and Complications
Post-treatment care is critical to ensure the dog recovers well. Complications can occur after treatment, making follow-up visits important.
Common Complications:
- Caval syndrome may require emergency care if a large number of heartworms block blood flow.
- Respiratory issues may arise as dead worms break down in the lungs.
After treatment, the dog may need:
- Restricted activity for several weeks.
- Regular annual testing to monitor for any remaining infection.
Veterinarians may also recommend precautions to prevent future infections. Regular heartworm prevention medications are important, as they help avoid re-infection and promote longer-term health.